Lifecycle Stages – are you using them correctly?
Succesfully tracking and measuring the effectiveness of the customer journey can be difficult, but with tools like Lifecycle Stages it becomes more manageble.
Lifecycle Stages is a way to categorise contacts based on how far they've progressed through your marketing and/or sales process. This is useful for a couple of reasons:
Lifecycle Reporting
It makes it easy to report on your Lifecycle Funnel, which gives you insight into where there is most friction in your customer journey. With this information in hand, you'll be able to make data driven improvements.
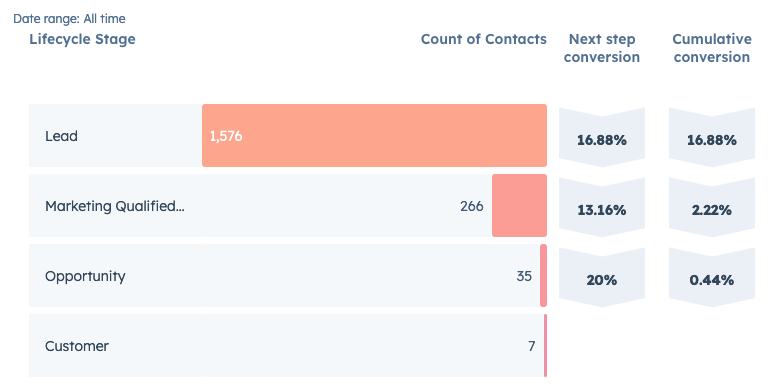
Illustration: A custom lifecycle stages report in HubSpot CRM
Sales to marketing hand-off
If you have defined that a Marketing Qualified Lead should be handed off to Sales (more on this later in the article), you only have to build one Marketing-to-Sales handoff process, which makes it easier to manage.
More relevant KPIs – no more vanity metrics
Some marketing teams are used to report on vanity metrics like number of likes on social media, number of page visits, number of conversions, etc. While many of these metrics makes sense to measure, they shouldn't be the driving metrics or foundational for your data driven desicions.
For a marketing team, focus on Marketing Qualified Leads, i.e leads handed off to sales. If you're using HubSpot, you can also tie ad accounts back to lifecycle stages and have the platform algorithms optimize for MQLs generated, which will in turn optimize for a better bottom line result for the company.
I'd argue that Lifecycle Stages is one of the foundational concepts required to describe the customer journey, track it's effectiveness and report on it clearly. In this article, I'll go through each of the stages and how you should be using them optimally.
Lifecycle Stage Definitions
As a HubSpot partner, we at Hubex usually think of Lifecycle Stages by HubSpot's definitions but I recognise that there might be other ways of thinkout out there. Therefore, it's important that all stakeholders in the company agree on the definition of each stage to ensure consistency and alignment.
That is why the first rule of Lifecycle Stages is that the entire company needs to be aligned on the definition of each stage in the Lifecycle Stage funnel. The second rule is that there is only rule one.
These are our definitions:
Subscriber
The subscriber stage represents individuals who have shown interest in your company by subscribing to a newsletter or other informational content. Subscribers are at the initial stage of engagement and can be nurtured to move further down the sales funnel. It is important to capture their attention and provide valuable content to encourage their progression.
Lead
A lead is any contact that has been created in your database. Typically, leads are generated through actions such as downloading ebooks or white papers, or converting on other high value content. At this stage, the contacts might not be ready to be worked by sales, but they've shown interest for the content relevant for your buyer personas. Nurturing leads through targeted marketing campaigns and personalized communication is essential to move them closer to becoming qualified leads.
Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL)
A marketing qualified lead is a contact that has been qualified by the marketing team, usually through predefined rules or automation. Marketing Qualified Leads have converted with buying intent. This means they've filled out a "Contact us" form, or signed up for a demo. When a lead reaches the MQL stage, it triggers an automated marketing-to-sales handoff process, ensuring a smooth transition and effective collaboration between the marketing and sales teams.
Sales Qualified Lead (SQL)
A sales qualified lead is a lead that has been qualified by the sales team. It occurs when the assigned sales representative accepts a marketing qualified lead and starts actively working it. The acceptance rate of sales qualified leads can be measured to assess the effectiveness of the lead qualification process. At this stage, it is important for the sales team to engage with the lead personally, understanding their needs and offering tailored solutions to move them closer to conversion.
Opportunity
When a contact has been successfully engaged and there is potential for a deal, they are categorized as an opportunity. At this stage, a deal is created in the CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system, and further sales efforts are focused on converting the opportunity into a paying customer.
Customer
The customer stage marks the point where the contact has made a purchase and become a paying customer. The deal is closed in the CRM, and the customer relationship shifts to a post-sales focus. Providing exceptional customer service, ongoing support, and delivering on promises are crucial at this stage to foster customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Evangelist
Evangelists are the happy customers who not only continue to engage with your company but also actively promote and share their positive experiences. These customers are valuable assets as they serve as advocates for your brand, attracting new customers through word-of-mouth and positive referrals. Recognizing and nurturing evangelists can help in building a strong and loyal customer base.
So, are you using the Lifecycle Stages correctly?
I've seen a lot of companies with a slightly different definition for their Lifecycle Stages. One of the usual implementations is to consider a Sales Qualified Lead "a lead that is ready for marketing to sales handoff". I'm not a fan of this definition, simply because you're missing out on a simple way of measuring the "acceptance rate" on leads that is handed off to sales. If your conversion rate from Marketing Qualified Lead to Sales Qualified Lead is low, you're not sending high quality leads to your sales team. If you're able to effectively measure this rate, you can adjust and prioiritize your marketing channels on the quality of the leads, not just quantity.
Instead, I'd advocate for this model:
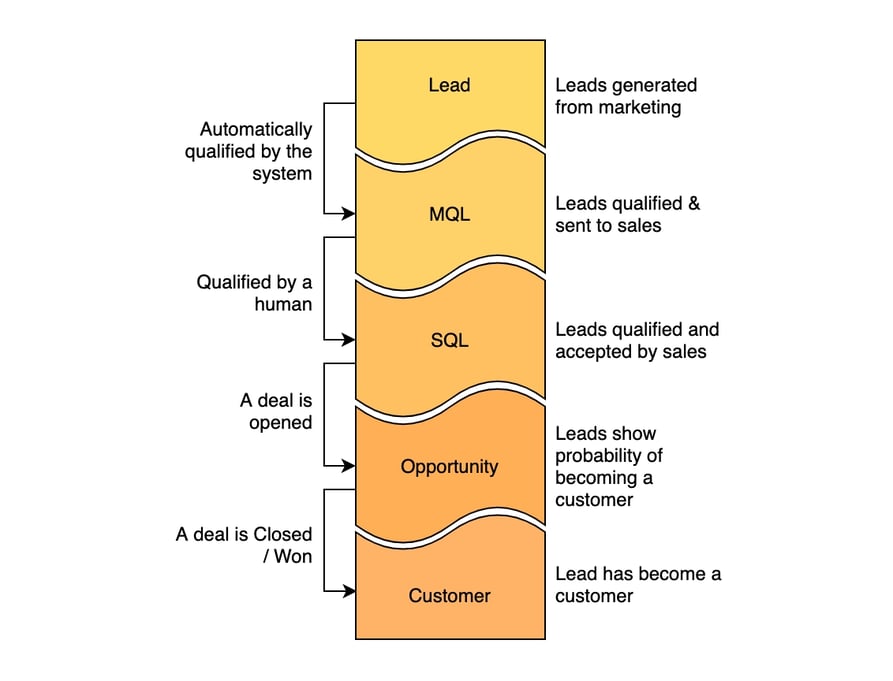
By setting up automation for qualifing contacts, you have a great mechanism to build a marketing-to-sales handoff process. If the receiving sales representative works the contact, use automation to set the lifecycle stage to SQL.
In the end, there's only one thing that matters. All internal stakeholders must agree on the Lifecycle Stage definitions, otherwise the data will be unusable.
How is your company using Lifecycle Stages?





